Products: Air Pollution Control, Flue Gas Treatment
Industry: Cement & Lime
Location: Isola delle Femmine, Italy
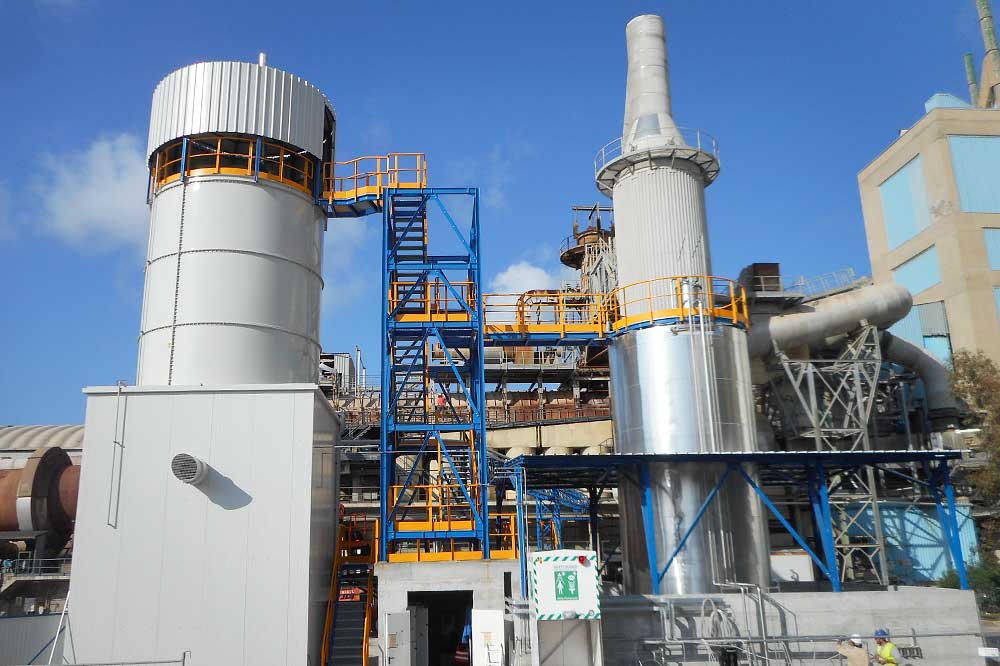
Boldrocchi succeeded in obtaining impressive NOX reduction rates by using Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) in a Lepol cement kiln at the Isola delle Femmine plant. We were able to reduce NOX to 350 mg/Nm3, translating into an efficiency of > 60%, rivaling the best abatement possible with SNCR. The injection point was chosen where there was an optimal flue gas temperature window (850°C – 1000°C) to ensure reaction efficiency.
Currently in Europe, SNCR is used in over 100 cement kiln plants. In this specific project, Boldrocchi used reagent with an ammonia content of 24,5 ± 0,4 % NH3 and maximum flowrate of 525 l/h and succeeded in reducing NOX to 350 mg/Nm3. These abatement results are impressive as SNCR is often only able to attain between 350 and 400 mg/Nm3 at best. For this kiln, the numbers mean an efficiency of > 60% (SNCR in general offers an efficiency between 30 and 65%, depending on the reagent, the amount of it and the temperature, along with other process parameters.)
Scope of supply:
- Ammonia solution storage tank
- Ammonia solution pumping system
- Skid for ammonia solution regulation
- Skid for demi water production
- System for ammonia solution nebulization and injection
Main process data:
Reagent: Ammonia Solution (NH4OH)
Ammonia content: 24,5 ± 0,4 % NH3
Max flowrate NH4OH: 525 l/h
Flue gas T° at injection point: 850 ÷ 1100°C
NOX after SNCR system: up to 350 mg/Nm3 corresponding to efficiency > 60%
This DeNOX system, contracted in 2016, is controlled from a local programmable logic controller (PLC) system. The logic, interlocks and control sequences are implemented in the local PLC, while alarms are acquired and sequences can be selected from the distributed control system (DCS).
Read more about Boldrocchi’s DeNOX technologies in our article “Eradicating NOX” in World Cement’s April 2018 issue.